Share
If you want to elevate your Avada websites, mastering dynamic data is essential. In a previous article, we looked at the dedicated Avada Dynamic Data Element. In this article, we explore how dynamic data as a whole transforms static website content into adaptable, data-driven content that update automatically across your site.
Let’s break down what dynamic data is, why it’s powerful, and how to use it effectively with Avada and WordPress.
Overview
Static vs Dynamic Content
Before diving in, it’s important to understand the difference between static and dynamic content.
What is Static content?
Static content is manually added to a page or post and never changes unless you edit it directly. For example, if you write a title or description into a text block, that same content appears everywhere the element is used.
What is Dynamic content?
Dynamic content, in contrast, adapts depending on the context. It is automatically generated based on the current view.
A simple example is the post title. When you use the dynamic data endpoint for a post title inside a blog post template, it will always display the title of the post being viewed—no manual updates needed.
Dynamic Data Options in Avada
Avada Dynamic Data lets you insert database-driven info into your website content. This system lets you automatically pull a wide range of data into your content—everything from post titles and featured images to custom fields, author names, and more.
While dynamic content can appear anywhere, it’s most commonly found in templates, such as Avada Layout Sections and Avada Post Cards, because these layouts can be reused across multiple posts or pages.
There are three primary methods to add dynamic data:
1. Avada Elements Options
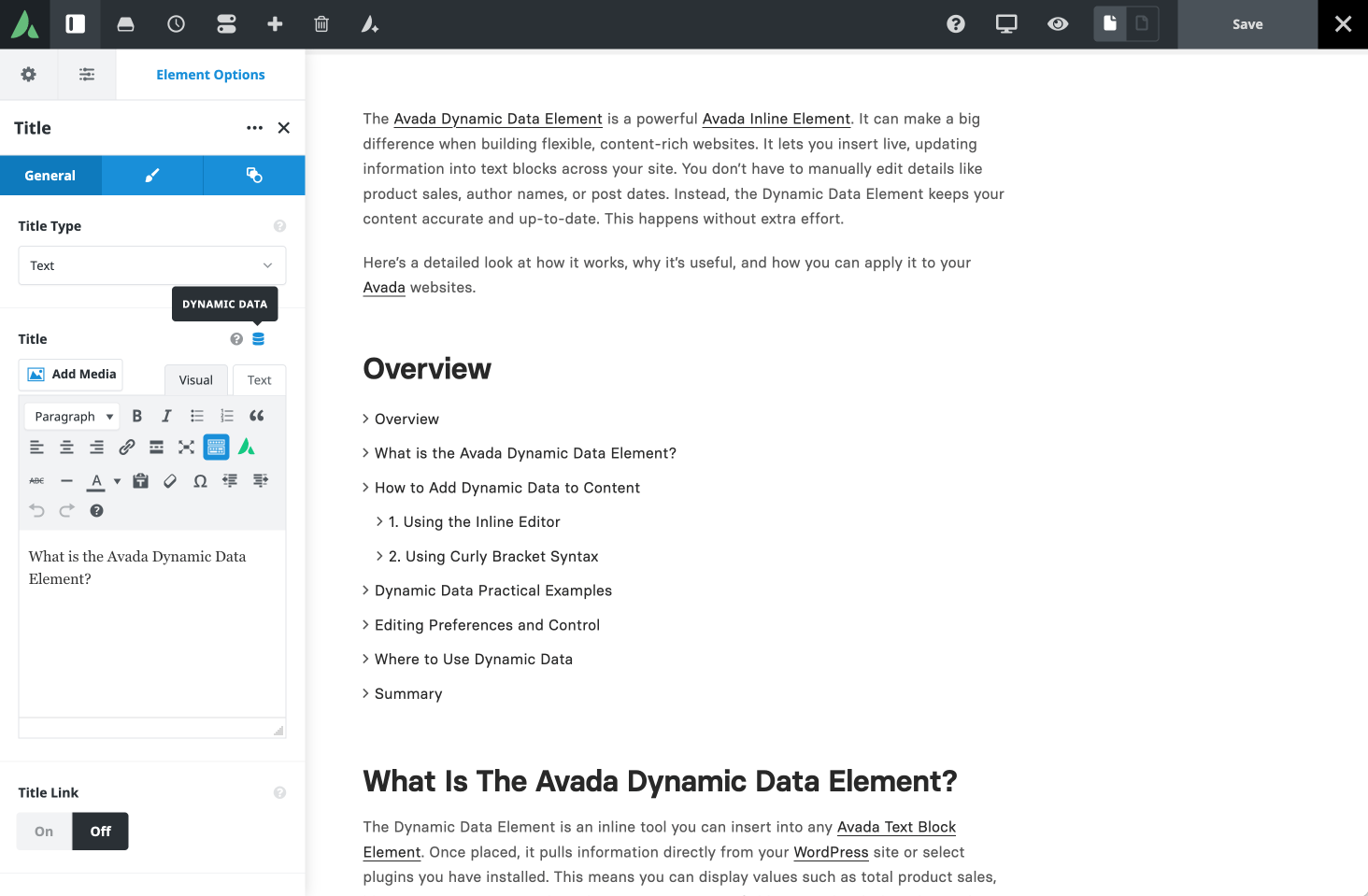
Most Avada Design Elements feature dynamic data options, marked by a database icon. This enables you to replace static text or images with dynamic information from your database. Let’s take a look at an example on the Avada Online School website.
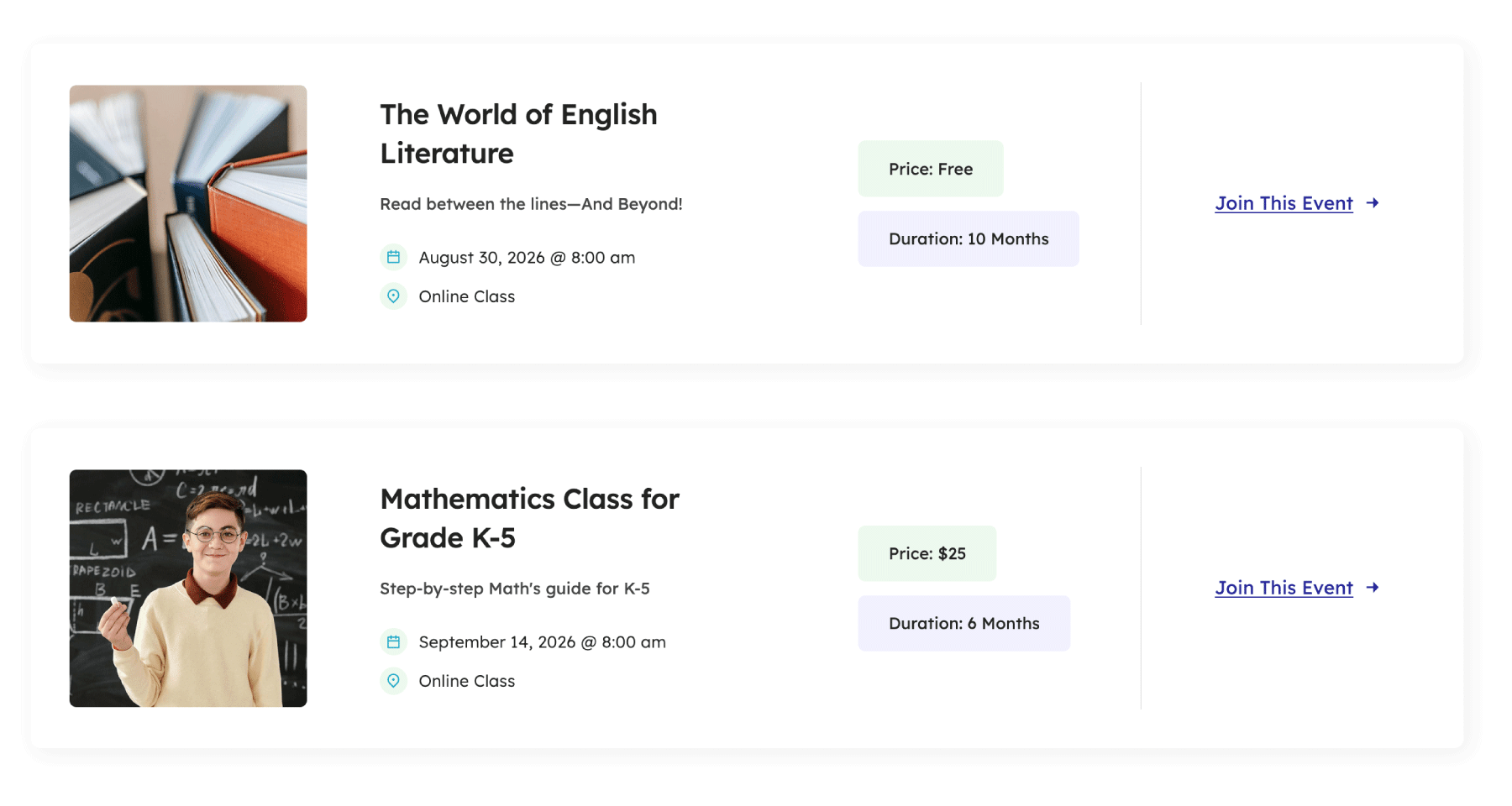
On the Online School Events page, an Avada Post Card Element displays a list of events. Each Post Card includes various Avada Design Elements—like a Title Element, Text Block Element, Checklist Element, and multiple Button Elements—all pulling different pieces of dynamic data.
Although the Post Card design is consistent, its content updates automatically for each event. This demonstrates dynamic data at work.
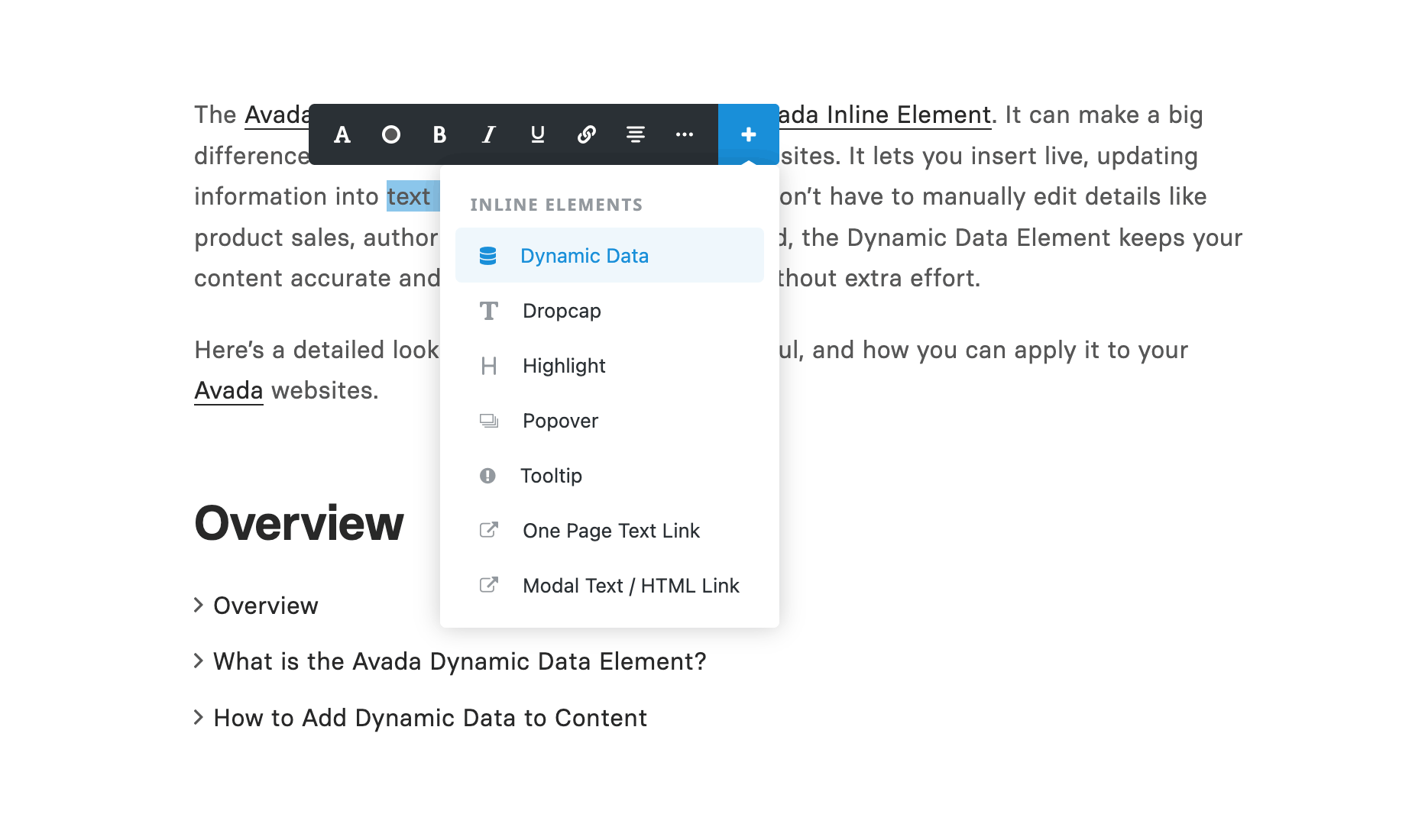
2. Dynamic Data Inline Element
Another powerful way to use dynamic data is to embed it directly in the text. Taking a closer look at the Avada Online School blog post example:
You’ll see a Title Bar Layout Section displaying blog post details. Instead of a Post Meta Element, you could instead add a Text Block Element and insert the Avada Dynamic Data Inline Element.
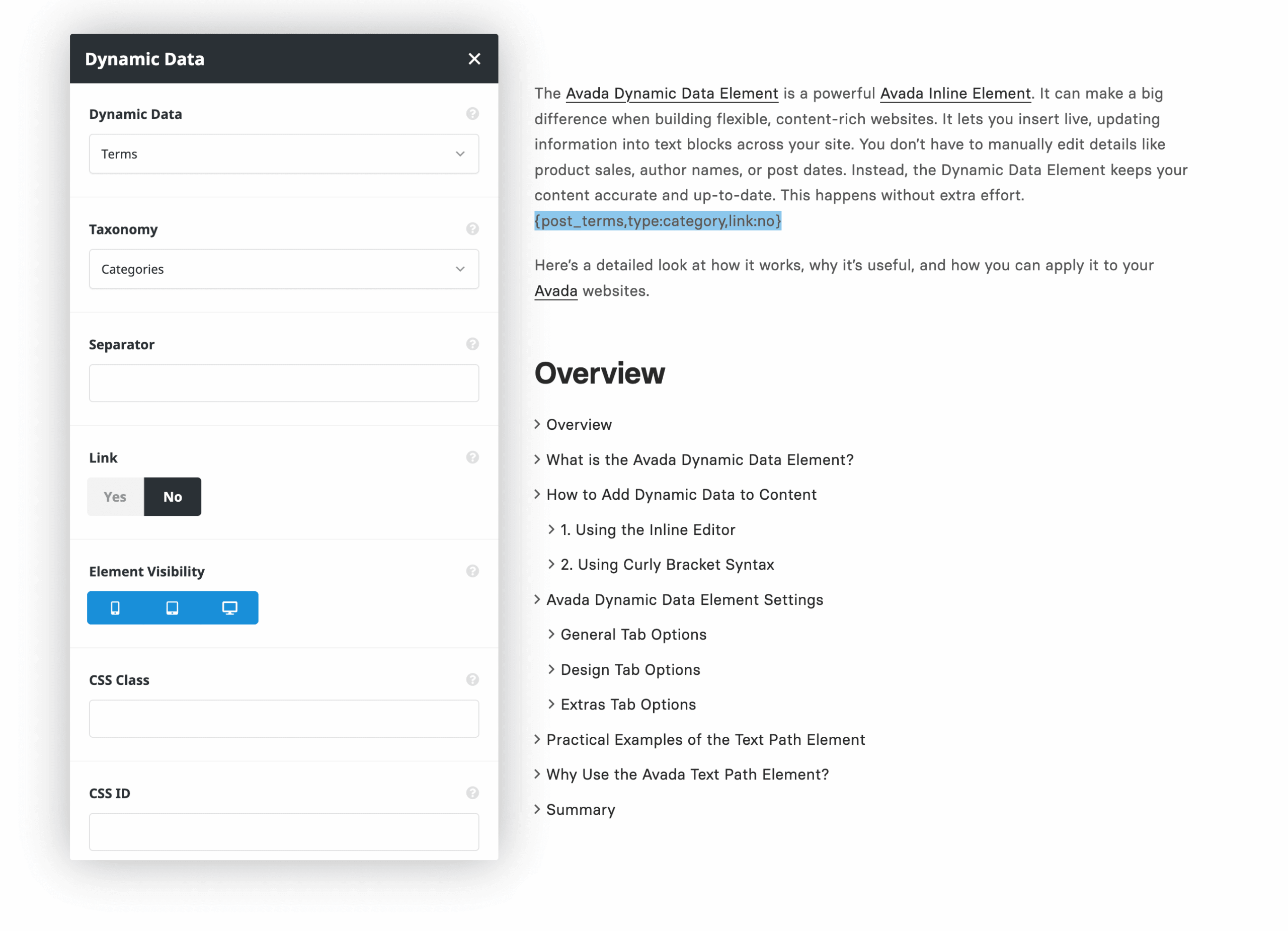
3. Using Curly Bracket Syntax
To use the syntax method, place your cursor and type a left curly bracket { to trigger dynamic data autocomplete. From there, select Post Date, or manually enter dynamic data syntax to show the post reading time directly in your text.
This flexibility allows you to combine multiple dynamic data points within a single sentence or paragraph, giving you complete control over how information is displayed.
Why Using Dynamic Data Is Useful
Dynamic data saves time, reduces errors, and ensures your site content stays consistent and up to date—automatically. Avada Dynamic Data can be used virtually anywhere on a site, including:
Whether you’re creating a blog, an online store, or a complex event site, dynamic data helps you scale your content and design seamlessly by combining multiple endpoints. Users can create highly customized blocks of content that automatically update as site data changes.
Summary
Dynamic data in Avada is both powerful and versatile. It lets you design templates that automatically adapt to your content, giving your site a professional, data-driven edge.
There are various approaches to using it—depending on your goals and site structure—but once you integrate dynamic data into your content, you’ll quickly notice how it streamlines your content strategy and overall maintenance.