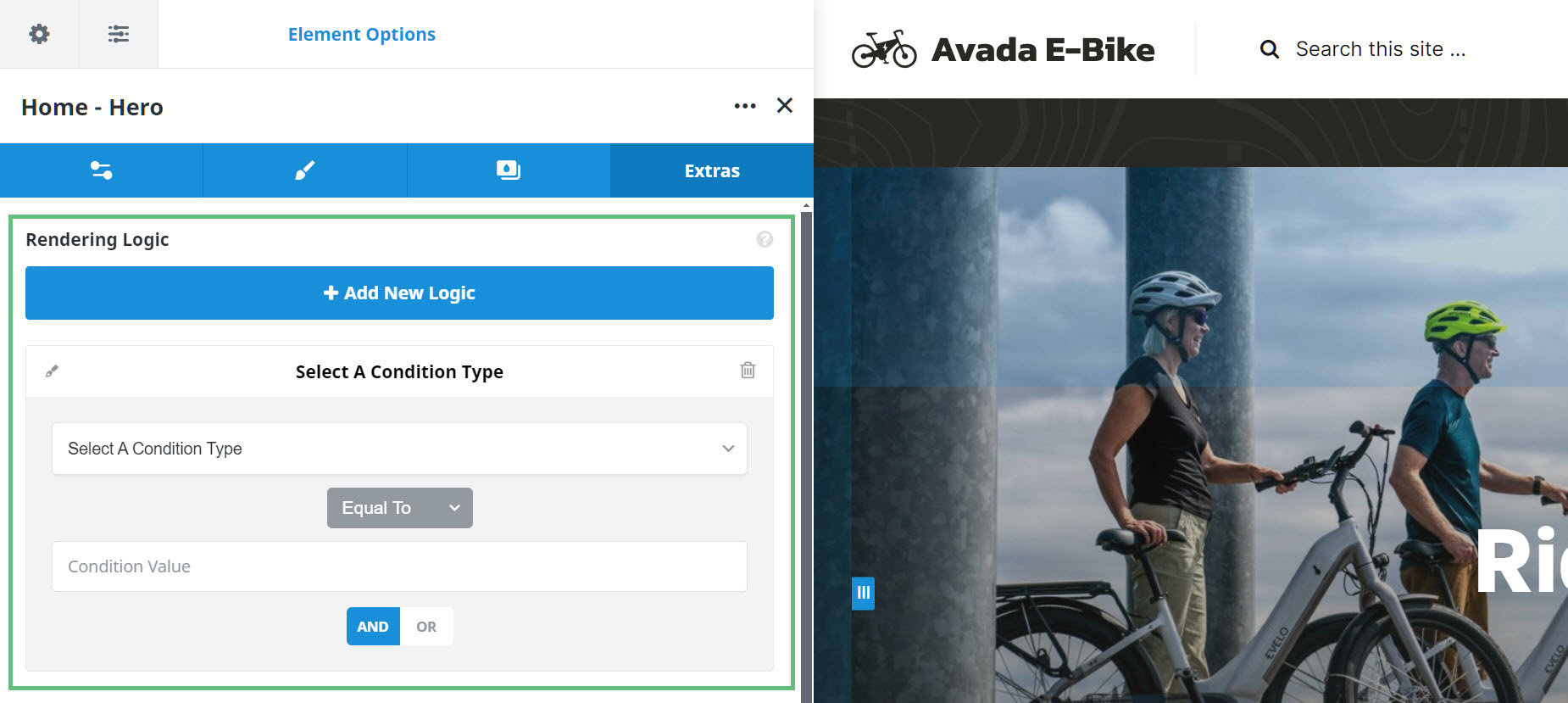
In the list below, you can see all the available Condition Types. There is a variety of Relational Operators and Condition Values. As you can imagine, there are many scenarios in which this feature could be used to control the contents of the Container or Column Element. The way to think of it is “I want to render this container if…”
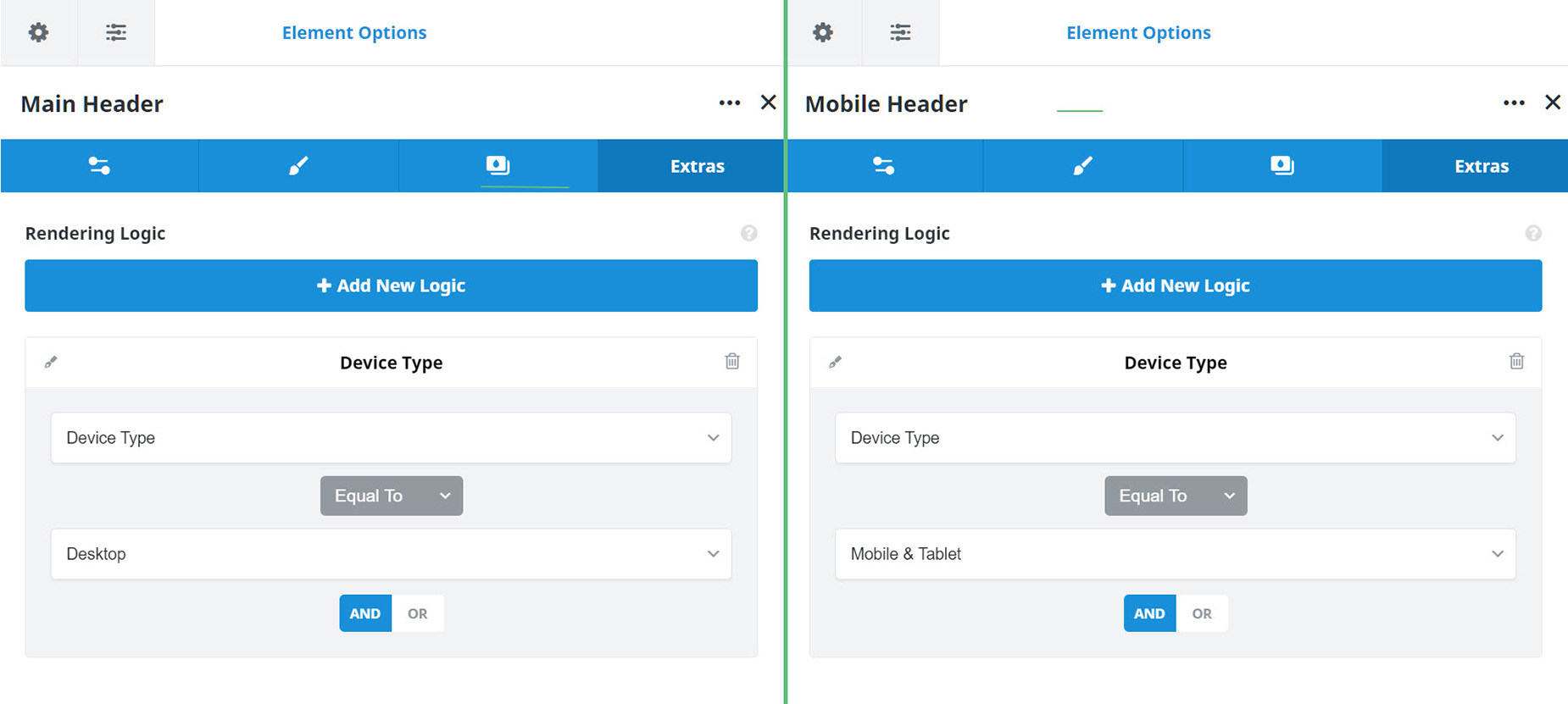
Device Type – Possibly the most basic of all conditional rendering, this allows you to set whether the content renders or not on a particular device type (size). The relational operators are Equal To and Not Equal To, and the possible values are Desktop, Mobile & Tablet, Tablet and Mobile.
GET Variable – This lets you check for a custom variable and value defined in the URL’s query string. It can particularly be useful when redirecting visitors after a form submission or similar. The relational operators are Equal To, Not Equal To, Greater Than, Less Than and Contains.
SESSION Variable – This lets you check for a custom variable and value stored server-side and linked to the session. The relational operators are Equal To, Not Equal To, Greater Than, Less Than and Contains.
User Agent – The User Agent is a short, technical description of the web browser, operating system, (and maybe mobile device) that you’re using as you access the internet. The relational operators are Equal To, Not Equal To, Greater Than, Less Than and Contains, and the Condition value will be the user agent you want to check for.
Referrer – The referrer is the webpage that sends visitors to your site using a link. In other words, it’s the webpage that a person was on right before they landed on your page. The relational operators are Equal To, Not Equal To, and Contains, and the Condition Value is the Referrer URL.
User Role – This is the WordPress User Role. The relational operators are Equal, and Not Equal To, and the Condition Values are whatever user roles you have registered on your website, such as Administrator, Editor, Author, Contributor etc.
User State – This refers to whether the user is logged in or not. The relational operators are Equal To and Not Equal To, and the Condition Values are Logged In, and Logged Out.
User Mata– This allows you to pull from the user Metadata, such as Username, Last Name, Nickname, Email etc.
User Meta Custom Key – This allows you to use a relational operator between a Meta Data Key and a Meta Value.
Custom Field – Check the value of a WP custom field variable. The relational operators are Equal To, Not Equal To, Greater Than, Less Than and Contains.
Post Published Date – This can be used to check against the publishing date of a post or page. A field lets you specify the format you want to use, so you can limit the check to the year, e.g., the second. The relational operators are Equal To, Not Equal To, Greater Than and Less Than, and the Condition Value also accepts the same inputs as strtotime().
Post Modified Date – This can be used to check against the the last modification date of a post or page. A field lets you specify the format you want to use, so you can limit the check to the year, e.g., the second. The relational operators are Equal To, Not Equal To, Greater Than and Less Than, and the Condition Value also accepts the same inputs as strtotime().
Post ID – This can be used to select the Post ID.
Post Type – This can be used to select the Post type.
Post Category – This can be used for the Post Category. The relational operators are Equal To and Not Equal To, and the Condition Values will be a list of Post Categories on your site.
Post Tag – This can be used for your post tags. The relational operators are Equal To and Not Equal To, and the Condition Values will be a list of the post tags on your site.
Post Term – This can be used for your post terms. The relational operators are Equal To and Not Equal To, and the Condition Value is a Term ID.
Post Count – This can be used to check whether an archive page has more or less posts than specified by you. The relational operators are Equal To, Not Equal To, Greater Than and Less Than, and the Condition Value is a number.
Term Count – This can be used to check against the total number of terms on a taxonomy archive. The relational operators are Equal To, Not Equal To, Greater Than and Less Than, and the Condition Value is a number.
Term ID – This can be used for your Term ID. The relational operators are Equal To and Not Equal To, and the Condition Value is a Term ID.
Featured images Count – This can be used to check against the number of Featured images that have been set. The relational operators are Equal To, Not Equal To, Greater Than and Less Than, and the Condition Value is a number.
Comment Status – This can be used for the status of a comment. The relational operators are Equal To and Not Equal To, and the Condition Values are Open or Closed.
Comments Count – This can be used to check against the number of comments related to a given post. The relational operators are Equal To, Not Equal To, Greater Than and Less Than, and the Condition Value is a number.
Number Of Headings – This can be used to check against the number of headings used on a given post. This is particularly useful, if you want to display a Tabel of Contents element conditionally. The relational operators are Equal To, Not Equal To, Greater Than and Less Than, and the Condition Value is a number.
Cart Status – This can be used based on the status of the Cart. The relational operators are Equal To and Not Equal To, and the Condition Values are In or Empty.
Sale Status – Similarly, this can be used based on the Sale status. The relational operators are Equal To and Not Equal To, and the Condition Values are Started or Ended.
Stock Quantity – This can be used based on the stock quantity of a product. The relational operators are Equal To, Not Equal To, Greater Than and Less Than, and the Condition Value is simply a number.
Stock Status – This can be used based on the status of stock. The relational operators are Equal To and Not Equal To, and the Condition Values are In Stock or Out Of Stock.
Product Purchase Status – This can be used based on the purchase status of a product. You can add a specific ID for a product, or you can leave the field empty to use the current product. The relational operators are Equal To and Not Equal To, and the Condition Values are Purchased or Not Purchased.
Product Type – This can be used based on the type of the product. The relational operators are Equal To and Not Equal To, and the Condition Values are Simple Product, Grouped Product, External/Affiliate Product or Variable Product.
Product Category – This can be used for the Product Categories. The relational operators are Equal To and Not Equal To, and the Condition Values will be a list of Product Categories on your site.
Product Tag – This can be used for your product tags. The relational operators are Equal To and Not Equal To, and the Condition Values will be a list of the product tags on your site.
Free Shipping Min. Amount – This can be used in conjunction with the WooCommerce Free Shipping Minimum Amount, inclucing Full, Missing and Percentage.
Related Products – This can be used for your related products. The relational operators are Equal To, Not Equal To Greater Than and Less Than, and the Condition Value is a number.
Up-Sells Products – This can be used for your Up-Sells products. The relational operators are Equal To, Not Equal To Greater Than and Less Than, and the Condition Value is a number.
Cross-Sells Products – This can be used for your Cross-Sells products. The relational operators are Equal To, Not Equal To Greater Than and Less Than, and the Condition Value is a number.
Product Variations – This can be used for your Product Variations. The relational operators are Has and Has Not, and the Condition Value is the Attrbute name eg. color or size.
Order Received Status – This can be used for the Status of the received order. The relational operators are Equal To and Not Equal To, and the Condition Values are Pending Payment, Processing, On Hold, Completed, Cancelled, Refunded, Failed, or Draft.
Order Received Total Value – This can be used for the total value of your recieved order. The relational operators are Equal To, Not Equal To Greater Than and Less Than, and the Condition Value is the total value of the order. Note. This only works on the Order Received Page (after user checks out).
Order Received Download Count – This can be used for the total number of items in your recieved order. The relational operators are Equal To, Not Equal To Greater Than and Less Than, and the Condition Value is the number of items that can be downloaded on the order receieved page. Note. This only works on the Order Received Page (after user checks out).
Event Status – This can be used based on the status of your event. The relational operators are Equal To and Not Equal To, and the Condition Values are Started or Ended.
ACF Field – This can be used for your ACF Fields. There is a Field Name field, and the relational operators are Equal To, Not Equal To Greater Than, Less Than and Contains. The Condition Value is needs to match the type of the field.
ACF Repeater Count – This can be used to check against the number of rows available for a single repeater field. There is a Field Name field, and the relational operators are Equal To, Not Equal To Greater Than, Less Than and Contains. The Condition Value is is a number.
ACF Repeater Single Value – This can be used for your ACF Repeater Single Values. There is a field for the field name and value – field[1][name], and the relational operators are Equal To, Not Equal To Greater Than, Less Than and Contains. The Condition Value needs to match the type of the repeater sub field.
ACF Repeater Sub Field – This can be used for your ACF Repeater Sub Field. There is a Sub Field Name field, and the relational operators are Equal To, Not Equal To Greater Than, Less Than and Contains. The Condition Value needs to match the type of the repeater sub field.
ACF Relationship Count – This can be used to check against the number of available ACF Relationships. There is a Field Name field, and the relational operators are Equal To, Not Equal To Greater Than, Less Than and Contains. The Condition Value is a number.