Share
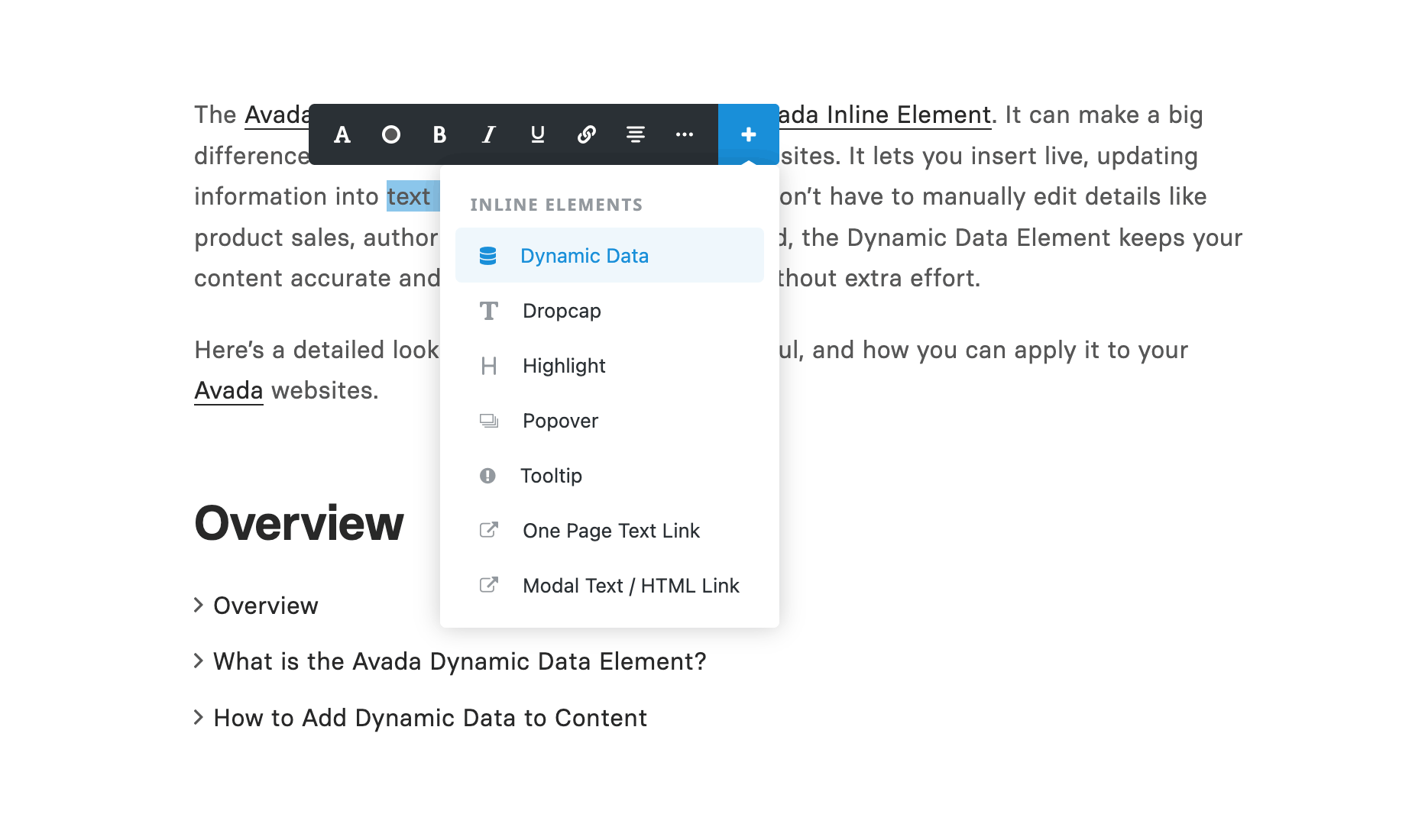
The Avada Dynamic Data Element is a powerful Avada Inline Element. It can make a big difference when building flexible, content-rich websites. It lets you insert live, updating information into text blocks across your site. You don’t have to manually edit details like product sales, author names, or post dates. Instead, the Dynamic Data Element keeps your content accurate and up-to-date. This happens without extra effort.
Here’s a detailed look at how it works, why it’s useful, and how you can apply it to your Avada websites.
Overview
What is the Avada Dynamic Data Element?
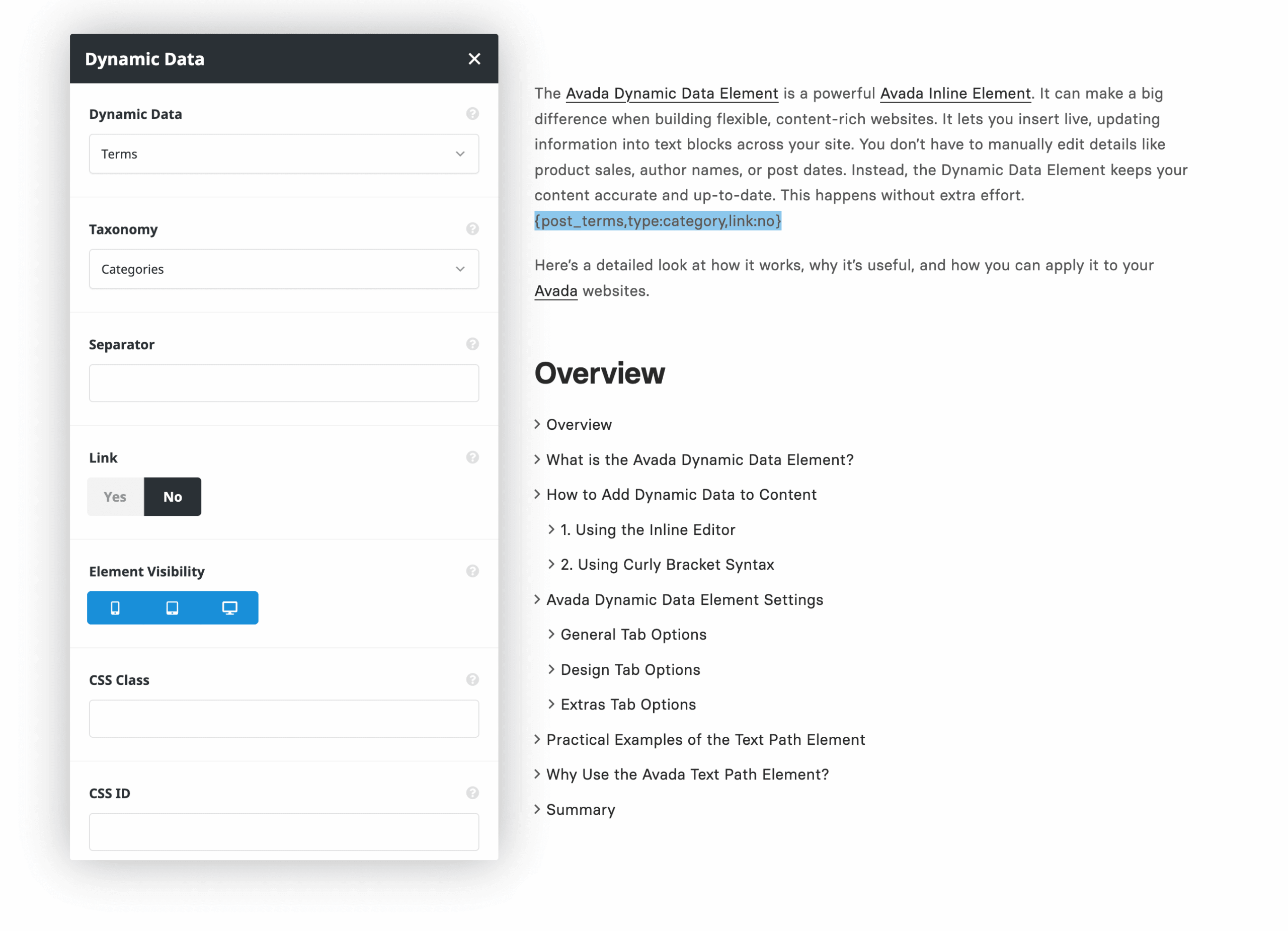
The Dynamic Data Element is an inline tool you can insert into any Avada Text Block Element. Once placed, it pulls information directly from your WordPress site or select plugins you have installed. This means you can display values such as total product sales, blog post categories, article authors, or even custom fields created with the Advanced Custom Fields (ACF) plugin.
This Avada Element is flexible. You can use it in page content, blog layouts, product templates, and Avada Post Cards. Wherever text exists, you can embed dynamic data. This makes content smarter and more connected to the live site. Common endpoints include:
How to Add Dynamic Data to Content
There are two main ways to add the Dynamic Data element to your text:
1. Using the Inline Editor
2. Using Curly Bracket Syntax
This second method offers a faster way to insert dynamic data, particularly for users familiar with shorthand syntax.
Dynamic Data Practical Examples
To see the Element in action, the video below uses the Avada Country Butcher prebuilt website. Inside a product content layout, a placeholder is replaced with a number with the Product Total Sales endpoint.
After saving, the product page automatically displays the number of times each product has been purchased. Instead of entering sales numbers manually, the dynamic data keeps the information accurate in real time.
Another example came from a blog post layout with a string of text at the top of the blog post. It combines static and dynamic content. The snippet includes the post title, author name, publish date, categories, and estimated reading time. No manual edits are needed.
Editing Preferences and Control
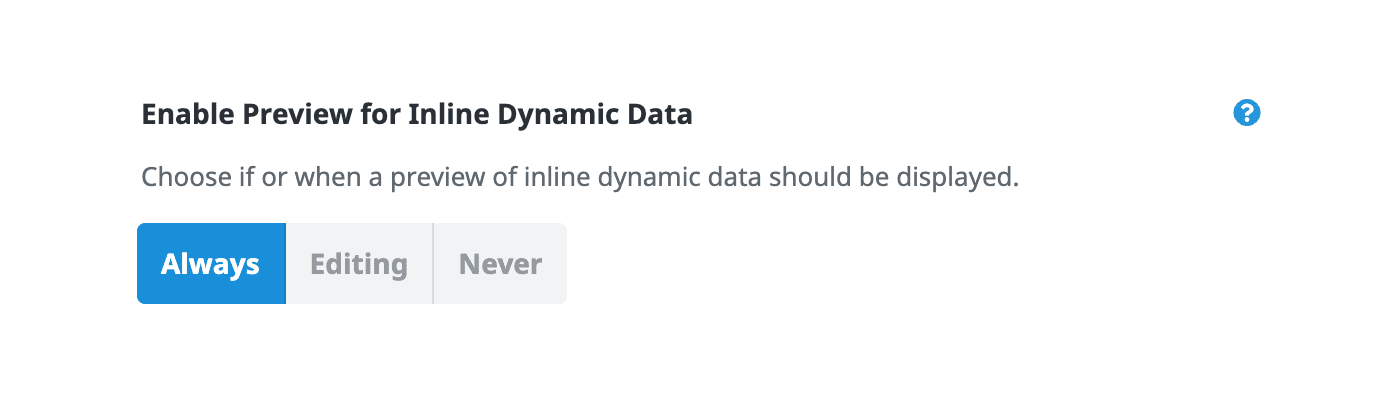
Avada also gives users the option to preview dynamic data while editing. Inside the builder preferences, there’s a setting called Enable Preview for Inline Dynamic Data, with three choices: always show a preview, show only while editing, or never preview at all. This makes it easy to decide whether you want to see the actual values in the editor or just the placeholder syntax while working. The options include:
For those who prefer a faster workflow, dynamic data can even be typed directly into the editor using its short syntax. While this doesn’t create a visible Inline Element in the editor, it produces the same result on the front end. Developers who know the endpoint names often find this the quickest way to insert content.
Where to Use Dynamic Data
The Avada Dynamic Data Element can be used virtually anywhere on a site, including:
With the ability to combine multiple endpoints, users can create highly customized blocks of content that automatically update as site data changes.
Summary
The Avada Dynamic Data element may seem simple at first glance, but it is one of the most versatile tools available in the builder. It allows you to merge static text with live data, pull multiple values into the same block, and adapt layouts so they always stay current. From showcasing real-time product sales to building dynamic post headers, it adds a layer of intelligence to your site content.
Whether you are a casual site builder or an advanced developer, this feature helps keep content accurate and engaging. Once you start using it, you will discover numerous ways to enhance your site’s dynamic, personalized, and professional appearance.